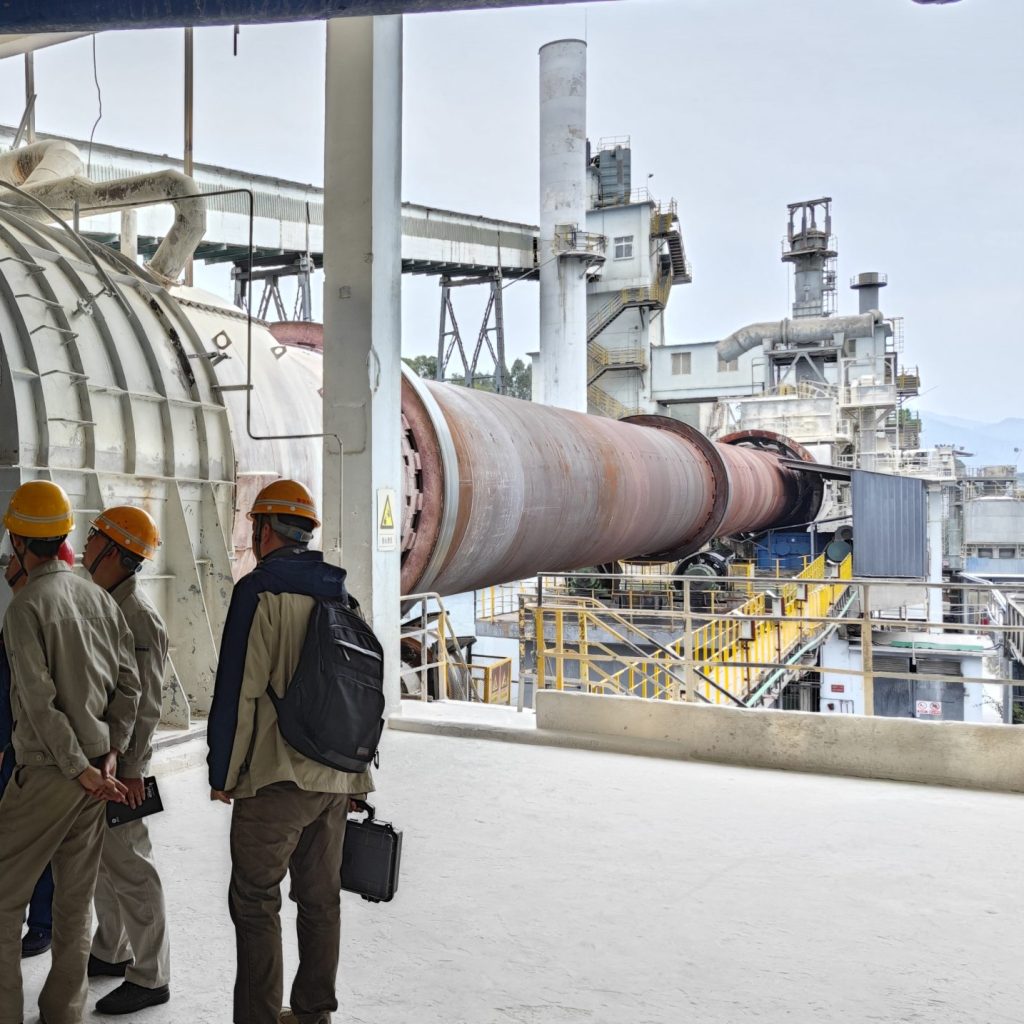
The advantages of pan-tilt temperature measurement
The advantages of pan-tilt temperature measurement with infrared pictures (i.e., using pan-tilt-mounted infrared thermal imaging cameras for temperature measurement) primarily include the following aspects:
- Large-Scale Area Scanning: Pan-tilt systems can achieve horizontal and vertical rotation (e.g., 360° horizontal rotation, ±90° vertical rotation), enabling comprehensive coverage of large scenes such as industrial sites, power facilities, or public areas, and eliminating fixed-angle monitoring blind spots via securtiy thermal imaging cameras.
- Adaptive to Complex Environments: In complex terrains or multi-obstacle scenarios (e.g., outdoor substations, stadiums, or warehouses), the pan-tilt can adjust its angle to bypass obstacles and target specific areas for precise temperature measurement. we can use pan tilt cctv camera.
- High-Resolution Thermal Imaging: Modern pan tilt zoom cemera system offer high thermal sensitivity (e.g., ≤0.05°C) and spatial resolution, enabling accurate identification of subtle temperature differences (e.g., overheating points in equipment or fever symptoms in human bodies).
- Real-Time Data Transmission: Combined with software systems, infrared images and temperature data can be transmitted to a control center in real time for immediate analysis, alerting, or recording, facilitating rapid decision-making (e.g., early fire detection or epidemic prevention screening).
- Avoiding Direct Contact Risks: Unlike contact thermometers, infrared temperature measurement requires no physical contact with targets, making it suitable for high-risk scenarios such as high-voltage equipment, infectious disease environments, or dangerous industrial sites, ensuring operator safety.
- Reduced Contamination Risks: In medical or food-processing environments, non-contact measurement minimizes cross-contamination risks, meeting hygiene standards.
- Programmable Patrol Routes: The pan-tilt can be pre-set with patrol paths and time intervals to automatically scan target areas, reducing manual labor and enabling 24/7 unattended monitoring (critical for applications like security, equipment maintenance, or energy management).
- Multi-Target Tracking & Alarm Triggers: Integrated with AI algorithms, the system can automatically track moving targets (e.g., personnel or vehicles), set temperature thresholds (e.g., ≥37.3°C for fever alerts), and trigger alarms (e.g., sound, light, or SMS notifications) for rapid response.
- Image & Data Archiving: Infrared pictures and temperature data can be stored for historical review, helping trace temperature changes over time (e.g., for equipment failure analysis or epidemiological investigations).
- Multi-Dimensional Data Output: Systems often support data export in formats like CSV or report generation, enabling further analysis via thermal distribution graphs, trend charts, etc., to optimize management strategies.
- Day-Night Continuous Operation: Infrared thermal imaging relies on object-emitted heat rather than visible light, performing consistently in low-light, backlit, or completely dark environments (e.g., night-time security or tunnel monitoring).
- Reduced Interference from Visible Light: Unlike visible-light cameras, infrared systems are unaffected by strong light (e.g., sunlight or searchlights), ensuring stable measurement accuracy.
- Compatibility with IoT/Cloud Platforms: Data can be integrated with IoT systems or cloud platforms for remote monitoring, big data analysis, or collaborative operations with other devices (e.g., alarms, drones, or ventilation systems).
- Multi-Sensor Fusion: Combined with visible-light cameras, laser rangefinders, or gas sensors, the system can provide multi-modal data for comprehensive scenario awareness (e.g., identifying overheating locations and visualizing site conditions).
- Industrial Inspection: Detecting overheating in power equipment, pipelines, or mechanical components.
- Public Health: Fever screening in airports, stations, or hospitals.
- Security & Fire Prevention: Early fire detection via abnormal heat source identification.
- Smart Cities: Monitoring urban infrastructure (e.g., electrical grids, waste treatment facilities) for energy efficiency and fault prediction.
In summary, pan-tilt infrared temperature measurement combines flexibility, precision, and automation, offering efficient, safe, and intelligent solutions for diverse industries.


