
 Project background
Project background
As an important part of the metallurgical industry, the temperature measurement of molten iron is completed by manual observation, thermocouples, and temperature guns. The working environment is harsh, and the temperature of molten iron needs to be measured many times. The labor intensity is high, the number of temperature measurements is small, and only 1 to 3 times are measured each time the iron is tapped. Continuous temperature measurement cannot be achieved. In addition, thermocouples are consumables, with high costs and relatively backward operation methods. The fluctuation of workers' operation norms makes the monitoring of molten iron temperature not accurate enough, and cannot reflect the temperature situation and change trend of the entire iron tapping process. In particular, the environment in front of the blast furnace is harsh, high temperature, and dusty, which is very dangerous. Since the ironmaking process in the blast furnace is fully enclosed, it is difficult to measure the temperature directly in the furnace. We need to understand and control the temperature state of molten iron through external temperature measurement. If the temperature of molten iron is too low, it will affect the smooth operation of the blast furnace. For a long time, it will cause serious consequences such as furnace body adhesion, abnormal furnace shape, abnormal furnace condition, and endangerment of safe production. In addition, molten iron temperature detection provides the most direct and effective detection method for low-silicon smelting. On the premise of ensuring sufficient physical temperature, the silicon content is reduced as much as possible, thereby reducing the coke ratio, which is beneficial to the steelmaking process. The temperature of molten iron is of great significance to the operation of blast furnaces, so it is necessary to establish a safe and intelligent continuous temperature measurement system for the taphole.
Solution
Our unit has developed a new type of continuous temperature measurement system for molten iron, leveraging thermal imaging cameras to directly measure the temperature of the iron flow at the taphole during tapping. This eliminates temperature drop and uniformity issues caused by the main ditch and slag skimmer, using an infrared thermography camera to more directly and accurately represent the furnace’s physical heat state and change process. Equipped with thermal cameras, the system features strong anti-smoke interference, long measurement distance, flexible target alignment, and precise readings. Molten iron temperature data is transmitted via signal lines to a host computer in the main control room, where a specialized program collects, processes, displays, and stores the information.
Advantagies

Critical Areas to Monitor: Furnace walls (hot spots = thinning) Conveyor bearings (heat = failing soon) Ladles (uneven heating risks cracks) Why This Beats Old Methods:Old way:✖ Shut down for inspections✖ Guess based on experience New way with thermal imaging small tech:✓ Scan during operation✓ See exact trouble spots Cost-Savin...

infrared thermal imaging technology improved detection efficiency, real-time monitoring, preventive maintenance, safety improvement and economic improvement

Every kiln operator knows that proper maintenance makes the difference between consistent results and costly downtime. In this guide, we'll explore how three specialized tools - small infrared cameras, kiln cement, and kiln Portland cement - can transform your maintenance routine and keep your kiln operating at peak efficiency. 1. Pr...
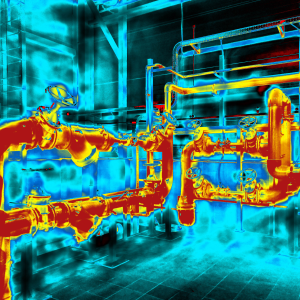
Invisible Dangers Thermal Cameras Reveal:✔ Gas leaks (shows as "cold clouds")✔ Tank leaks (wet areas look different)✔ Pump failures (abnormal heat patterns) Why Workers Love These Tools: Thermal imaging small cameras fit in tool belts No need to shut down equipment Takes 1/10th the time of old inspection methods Case Study:A refi...