Application scenarios of Long-wave infrared
Here are the key application scenarios for long-wave infrared (LWIR, typically 8–14 μm wavelength), leveraging its unique thermal imaging capabilities:
- Predictive Maintenance: Detect overheating in machinery (e.g., motors, bearings, electrical panels) to prevent failures and downtime.
- Firefighting: Locate hotspots in fires, identify survivors in smoke-filled environments, and assess structural integrity during emergencies.
- Hazardous Environments: Monitor chemical plants, refineries, or radioactive areas remotely without human exposure.
- Energy Audits: Identify heat leaks in walls, roofs, or insulation to optimize energy efficiency in buildings.
- Moisture Detection: Locate hidden water damage (e.g., leaks in pipes, damp walls) by analyzing thermal patterns.
- Solar Panel Inspection: Spot underperforming panels or faulty connections via temperature anomalies.
- Fever Screening: Rapid, non-contact temperature measurement for pandemic control (e.g., airports, hospitals).
- Medical Thermography: Aid in diagnosing vascular issues, inflammation, or skin disorders through thermal imaging.
- Veterinary Care: Assess animal health (e.g., fever, injuries) in livestock or wildlife without physical contact.
- Night Vision Systems: Enhance driver safety by detecting pedestrians, animals, or obstacles in low-light conditions.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Complement visible sensors for obstacle detection in fog, dust, or darkness.
- Aerospace Maintenance: Inspect aircraft components (e.g., engine heat patterns, ice buildup on wings).
- Crop Monitoring: Detect water stress, pest infestations, or nutrient deficiencies in plants via canopy temperature.
- Wildlife Tracking: Monitor nocturnal animals or endangered species without disturbance in remote habitats.
- Climate Research: Study urban heat islands, glacier melt, or volcanic activity using satellite-based LWIR.
- Border Patrol: Detect intruders or smuggled goods using thermal signatures in darkness or camouflage.
- Search & Rescue: Locate missing persons in rugged terrain or disaster zones through body heat detection.
- Military Reconnaissance: Identify enemy positions, vehicles, or infrastructure in stealth operations.
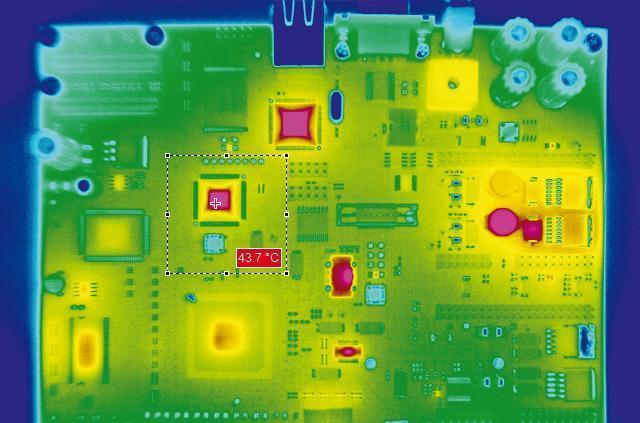
- Component Testing: Identify hotspots in PCBs, microchips, or batteries (e.g., lithium-ion cell defects in EVs).
- Quality Control: Ensure proper thermal interface material (TIM) application and heat sink performance.
- Data Center Optimization: Map server rack hotspots to improve cooling efficiency.
- Art Conservation: Reveal hidden layers, repairs, or moisture damage in paintings or historical artifacts.
- Archaeological Surveys: Detect buried structures or artifacts via subtle surface temperature variations.
- Material Science: Study thermal properties (e.g., emissivity, conductivity) of new materials or coatings.
- Biomedical Engineering: Develop non-invasive diagnostic tools or optimize thermal therapy techniques.
- Physics Experiments: Monitor phase changes, heat distribution, or reaction kinetics in lab settings.
- Handheld Thermal Imagers: Used by homeowners, electricians, or HVAC technicians for DIY inspections.
- Drone Imaging: Agricultural monitoring, roof inspections, or wildlife surveys via aerial thermal sensors.
- Non-Contact Operation: Safe for use on moving or high-voltage targets.
- All-Weather Capability: Effective in darkness, fog, or smoke (unlike visible-light cameras).
- Cost-Effective Sensors: Non-cooled detectors make LWIR accessible for portable and industrial use.
Long-wave infrared’s ability to visualize heat signatures without reliance on visible light makes it indispensable across industries requiring real-time, remote thermal analysis.

