What are the benefits of long wave temperature measurement?
The advantages of long-wave (LW) infrared thermometry, mwir camera (operating in the 8–14μm wavelength range) arise from its unique interaction with materials, atmospheric conditions, and sensor technology. Here are the key benefits:
- Most non-metallic materials (e.g., plastics, ceramics, paints, human skin) have high and stable emissivity in the 8–14μm band.
- This simplifies temperature measurement, as emissivity corrections are minimal or pre-calibrated for common surfaces.
- Example: In building diagnostics, LW thermography easily detects heat leaks through walls without complex surface adjustments.
- LW radiation is primarily reflected or emitted from the surface of solids (penetration depth < 1μm for most materials).
- This makes it ideal for non-destructive surface temperature mapping, such as:
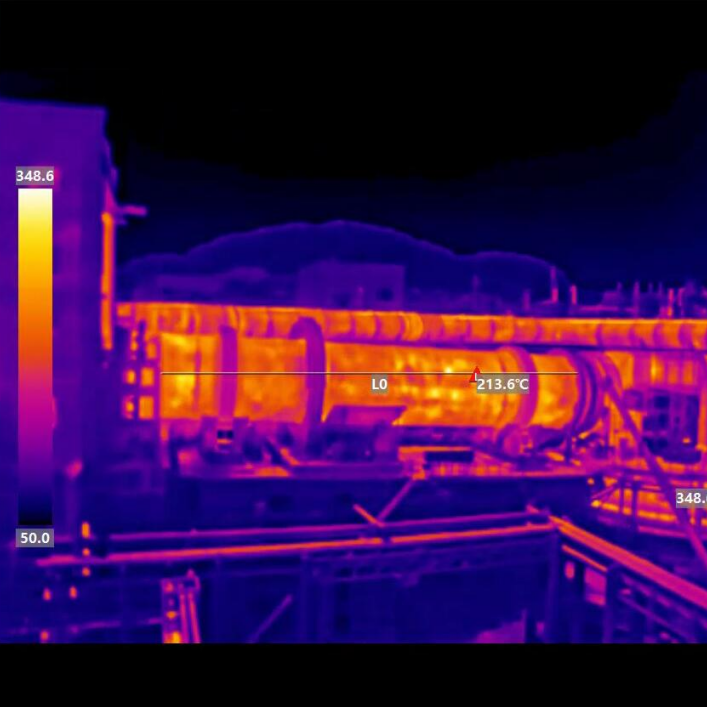
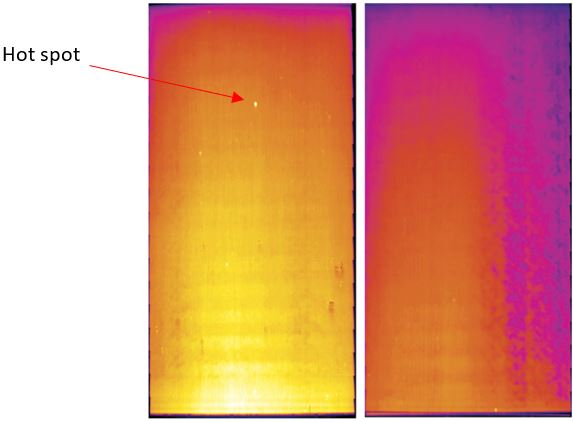
- Inspecting electrical panels for hotspots.
- Monitoring skin temperature in medical applications (e.g., fever screening).
- Quality control in manufacturing (e.g., detecting coating defects).
- While the 8–14μm band high definition infrared camera is slightly affected by water vapor, it remains effective in most ambient conditions (e.g., indoor environments, moderate humidity).
- Unlike medium-wave (MW) infrared, LW does not require specialized corrections for typical atmospheric moisture, making it user-friendly for general-purpose applications.
- LW detectors high speed thermal camera(e.g., microbolometers) are non-cooled and require no cryogenic cooling, reducing hardware complexity and cost.
- This enables compact, portable devices (e.g., handheld thermal cameras, drone-mounted LW sensors) widely used in:
- Firefighting (to visualize heat behind smoke).
- Renewable energy (solar panel efficiency checks).
- Automotive safety (night vision systems).
- The Planck radiation curve peaks in the LW range for objects at low to medium temperatures (20–1000°C).
- LW sensors excel at detecting subtle thermal differences in these ranges, e.g.:
- Monitoring cold storage leaks (-30°C to 0°C).
- Studying volcanic activity (lava at 500–1000°C).
- Analyzing electronic component hotspots (50–150°C). -mwir camera
- LW thermometry avoids physical contact with targets, making it suitable for:
- Hazardous environments (e.g., radioactive sites, high-voltage areas).
- Fragile objects (e.g., historical artifacts, delicate electronics).
- High-speed processes (e.g., conveyor belt quality control without disruption).
- Many industry standards (e.g., ISO 6781 for thermography) are based on LW technology, ensuring interoperability and calibration consistency across devices.
- Example: In predictive maintenance, LW thermal maps are widely recognized for documenting equipment health over time.
| Aspect |
Long-Wave (8–14μm) |
Medium-Wave (3–5μm) |
| Ideal Temperature Range |
Low to medium (20–1000°C) |
High (800–2000°C) |
| Emissivity for Metals |
Low and variable (requires correction) |
More stable (e.g., steel ≈ 0.1–0.3) |
| Detector Cooling |
Non-cooled (microbolometers) |
Often requires cooling (e.g., InSb, MCT) |
| Typical Applications |
Building inspection, human temperature, electronics-high definition infrared camera |
Furnaces, molten metal, aerospace guidance -high speed thermal camera |
Long-wave infrared thermometry excels in low-to-medium temperature measurement, surface-level analysis, and general-purpose thermal imaging due to its high emissivity for non-metals, cost-effective sensors, and robustness in typical atmospheric conditions. Its role in safety, maintenance, and scientific research highlights its versatility in scenarios where simplicity, affordability, and non-contact operation are critical.



